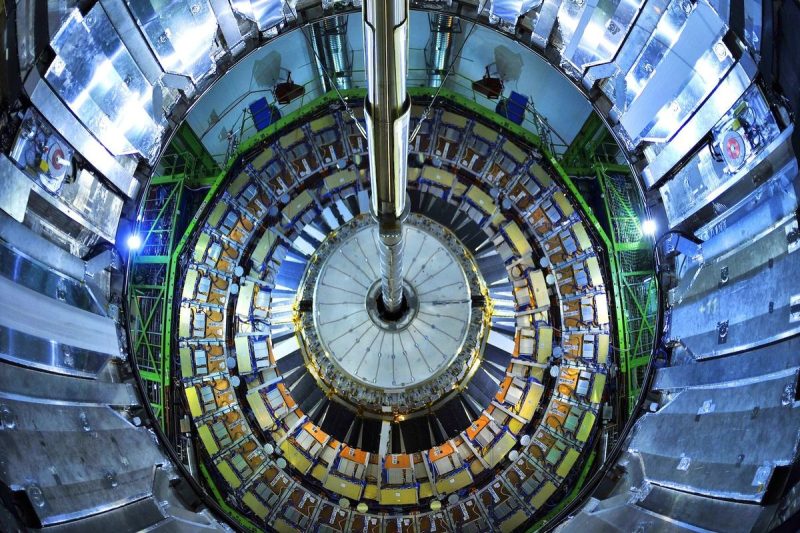
Scientists at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN have successfully transmuted lead into gold — not by alchemy, but by smashing heavy ions together at nearly the speed of light.
The process, confirmed by the ALICE collaboration and published in ‘Physical Review Journals,’ reveals that during Run 2 of the LHC (2015 to 2018), some 86 billion gold nuclei were produced via high-energy collisions between lead atoms.
While that amounts to just 29 trillionths of a gram, the feat marks the first time this rare transmutation process has been systematically measured and analyzed in a laboratory setting.
“Thanks to the unique capabilities of the ALICE zero degree calorimeters (ZDCs), the present analysis is the first to systematically detect and analyze the signature of gold production at the LHC experimentally,” said Uliana Dmitrieva, a physicist with the ALICE collaboration, which studies quark-gluon plasma and includes nearly 2,000 scientists.
The feat is a striking, if fleeting, vindication of chrysopoeia — the alchemical dream of converting base metals into gold.
For centuries, alchemists believed lead’s similar density to gold suggested a latent transformation was possible, if only they could find the right process or Philosopher’s Stone. In modern physics, the solution turned out to be neither mystical nor practical: an ultra-powerful particle accelerator and atomic violence on an unthinkable scale.
At the LHC, which lies beneath the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, lead nuclei are accelerated to 99.999993 percent the speed of light and made to collide inside ALICE. Most of these interactions are violent enough to recreate quark-gluon plasma, the exotic state of matter thought to have existed moments after the Big Bang.
But some collisions — described as ultraperipheral — involve near misses, where the lead atoms don’t directly touch, but instead interact via their extremely powerful electromagnetic fields.
Those interactions, known as electromagnetic dissociation, can strip protons and neutrons from lead nuclei. Since lead has 82 protons and gold has 79, it takes only a loss of three protons to transmute one into the other.
“It is impressive to see that our detectors can handle head-on collisions producing thousands of particles, while also being sensitive to collisions where only a few particles are produced at a time, enabling the study of rare electromagnetic ‘nuclear transmutation’ processes,” said ALICE spokesperson Marco van Leeuwen in a statement.
ALICE scientists used specialized ZDCs to track the transmutations, detecting emissions of zero, one, two or three protons — corresponding respectively to the continued presence of lead, or its conversion into thallium, mercury or gold.
The gold produced in these experiments doesn’t last long. The nuclei fly out of the collision zone at high energies and slam into the LHC’s beam pipe or other material downstream, instantly shattering into subatomic debris.
Still, the volume of gold created is increasing. During Run 3 of the LHC, which is ongoing, the accelerator is producing gold at nearly 89,000 nuclei per second, almost double the rate of the previous run due to improved collision energy.
From a commercial perspective, the process remains wildly inefficient.
To produce even a gram of gold would require over 30 quadrillion (30,000,000,000,000,000) such nuclear conversions, along with enormous amounts of energy and infrastructure. The entire gold yield from years of operation remains microscopic — far short of what would be needed to make even a flake of jewelry.
Nonetheless, the implications of the discovery go far beyond ancient mythology. The ability to measure such rare transmutations improves scientists’ understanding of nuclear interactions and helps refine the theoretical models used to predict beam behavior and energy losses in the LHC — a key factor in the design of future particle accelerators.
Securities Disclosure: I, Giann Liguid, hold no direct investment interest in any company mentioned in this article.